ஏப்ரல் 11,2010,00:00 ISThttp://www.dinamalar.com/world_detail.asp?news_id=5282
லண்டன்:நவீன ‘3டி’ கம்ப்யூட்டர் தொழில்நுட்பத்தை பயன்படுத்தி, ஓவியர்கள் குழு ஒன்று, இயேசுவின் முகத்தை வரைந்துள்ளது.இது குறித்து லண்டனிலிருந்து வெளியாகும், ‘டெலிகிராப்’ பத்திரிகையில் கூறப்பட்டுள்ளதாவது.இயேசு உயிர் நீத்தபின், அவரை கல்லறையில் அடக்க செய்யும் போது, அவரது உடல் மீது போர்த்தப்பட்டிருந்த லினன் ரக துணியால் ஆன போர்வையில், அவரின் உருவம் அமைப்பு பதிந்ததாக நம்பப்படுகிறது. அதை பயன்படுத்தி, இந்த ஓவியர்கள் குழு, தற்போது இயேசுவின் முகத்தை, ‘3டி’ கம்ப்யூட்டர் தொழில்நுட்பத்தின் மூலம் வரைந்துள்ளனர்.
இதை பதிவு செய்த, ‘டிவி’ சேனல் ஒன்று,’தி ரியல் பேஸ் ஆப் ஜீசஸ்’ என்ற பெயரில் அதை ஒளிபரப்பியது.இதுகுறித்து, இத்திட்டதின் தலைமை ஓவியரான, ரே டவுனிங் கூறுகையில்,’இயேசுவின் முகத்தை மீண்டும் வரைய விரும்பினால், அதற்கு அவரது உண்மையான முகம் தேவை. அதற்கு தற்போது ஆதாரமாக இருக்கும் ஒரே பொருள், இயேசுவின் உடலில் போர்த்தப்பட்டிருந்த போர்வை தான்’ என்றார்.இவ்வாறு பத்திரிகையில் கூறப்பட்டுள்ளது.
டூரின் சிரௌட் (turin shroud)எனப்படும் அந்த துணி 13ம் நூற்றாண்டில் உருவாக்கப் பட்ட போலி என்று மூன்று பரிசோதைக் கூடங்களில் நடத்தப் பட்ட ஆய்விலிருந்து சில தெரிவிக்கப் பட்டது (carbon dating showing the shroud is from 1260-1390). அதனை வாடிகனுன் ஏற்றுக் கொண்டது. அது மட்டுமல்லாது, அதில் படிந்துள்ள ரத்தக் கரை மனிதனுடையர்தல்ல என்றும் நிரூபிக்கப் பட்டது. பிறகு எப்படி அத்தகைய போலியான் ஒன்றிலிருந்து ஏதோ ஒன்று வரமுடியும்? விஞ்ஞானம் என்று சொல்லி இப்படியும் பொய் சொன்னால் என்னாவது?
The Shroud of Turin
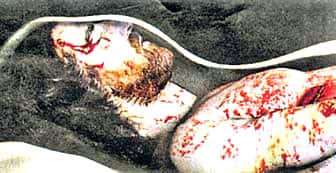
 Image from the Shroud. This is also a low magnification shot taken of a blood-image area 3-FB (small of the back) taken by Pellicori and Evans in 1978. Note the red color unlike dried blood which is brown, magnification 10X.
Image from the Shroud. This is also a low magnification shot taken of a blood-image area 3-FB (small of the back) taken by Pellicori and Evans in 1978. Note the red color unlike dried blood which is brown, magnification 10X.According to Dr. Walter McCrone and his colleagues, the 3+ by 14+ foot cloth depicting Christ’s crucified body is an inspired painting produced by a Medieval artist just before its first appearance in recorded history in 1356.
The faint sepia image is made up of billions of submicron pigment particles (red ochre and vermilion) in a collagen tempera medium. The pigments red ochre and vermilion with the collagen tempera medium was a common paint composition during the 14th century; before which, no one had ever heard of the Shroud.
Initial Examination – 1979
Dr. McCrone determined this by polarized light microscopy in 1979. This included careful inspection of thousands of linen fibers from 32 different areas (Shroud and sample points), characterization of the only colored image-forming particles by color, refractive indices, polarized light microscopy, size, shape, and microchemical tests for iron, mercury, and body fluids. The red ochre is present on 20 of both body- and blood-image tapes; the vermilion only on 11 blood-image tapes. Both pigments are absent on the 12 non-image tape fibers. The paint pigments were dispersed in a collagen tempera (produced in medieval times, perhaps, from parchment). It is chemically distinctly different in composition from blood but readily detected and identified microscopically by microchemical staining reactions. Forensic tests for blood were uniformly negative on fibers from the blood-image tapes. Based on these findings, McCrone postulated that the Shroud was painted in 1355.

From: McCrone, Walter C. The Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Supplemented by the Polarized Light Microscope (PLM), and Vice Versa. Scanning Microscopy, 7(1): 1-4, fig. 3. 1993.
Further Research in 1980
In 1980, using electron microscopy and x-ray diffraction, McCrone found red ochre (iron oxide, hematite) and vermilion (mercuric sulfide); the electron microprobe analyzer found iron, mercury, and sulfur on a dozen of the blood-image area samples. The results fully confirmed Dr. McCrone’s results and further proved the image was painted twice – once with red ochre, followed by vermilion to enhance the blood-image areas.
In 1987, carbon dating at three prestigious laboratories agreed well with his date: 1355 by microscopy and 1325 by C-14 dating. The suggestion that the 1532 Chambery fire changed the date of the cloth is ludicrous. Samples for C-dating are routinely and completely burned to CO 2 as part of a well-tested purification procedure. The suggestions that modern biological contaminants were sufficient to modernize the date are also ridiculous. A weight of 20th century carbon equaling nearly two times the weight of the Shroud carbon itself would be required to change a 1st century date to the 14th century (see ‘Amount of Modern Biological Contaminant Required to Raise the Date of a 36 A.D. Shroud’). Besides this, the linen cloth samples were very carefully cleaned before analysis at each of the C-dating laboratories.

This graph shows the effect of the measured 1st Century linen cloth of added 20th Century carbon (mold, mildew, bacteria, etc.). The “Shroud” weighs about 20 pounds (9 kg.). Approximately 40 pounds (18 kg.) of 20th Century carbon contaminant would be required to raise the measured carbon date to 14th Century.
Experimental details on the tests carried out by McCrone are available in five papers published in three different peer-reviewed journal articles: The Microscope 28, p. 105, 115 (1980); The Microscope 29, p. 19 (1981); Wiener Berichte uber Naturwissenschaft in der Kunst1987/1988, 4/5, 50 and Acc. Chem. Res. 1990, 23, 77-83.
Conclusion:
The “Shroud” is a beautiful painting created about 1355 for a new church in need of a pilgrim-attracting relic.
The reaction of the ‘world’—Quotes on Dr. McCrone’s work on the Shroud
Now you can read the Judgement Day for the Turin Shroud book and hear Dr. McCrone’s account of the microanalytical research on the Shroud.
An excerpt from the book is included here:
“This book makes three major contributions. Firstly, it provides a clear, easily understood description of the analytical methods that have been used on the Shroud. Secondly, it reviews the scientific debates surrounding these methods, the analytical results obtained, and the interpretations made by the scientists. Thirdly, it serves as an excellent example of the scientific, personal and social issues that come into play when emotions, prejudices and perceptions of science interact with classical scientific methods and ethics.
As one who has spent his entire professional life as a consulting analytical chemist and microscopist, Dr. McCrone has regularly seen differences in opinions arise among scientists, and, more importantly, seen objective scientists resolve these differences, professionally and honestly.” Judgement Day for the Turin Shroud, Foreward, p. xviii











 existed before the 8th century, according to Danin, there is "clear evidence that the shroud originated before the eighth century." The cloth is believed to have been in a chest of relics from at least the time of the Moorish invasion of Spain. It is said to have been in the chest when it was opened in 1075. But, since there is no blood on the shroud of Turin and there is no good reason to accept Danin's assumption that the pollen grains were on the Shroud from its origin, this argument is spurious.
existed before the 8th century, according to Danin, there is "clear evidence that the shroud originated before the eighth century." The cloth is believed to have been in a chest of relics from at least the time of the Moorish invasion of Spain. It is said to have been in the chest when it was opened in 1075. But, since there is no blood on the shroud of Turin and there is no good reason to accept Danin's assumption that the pollen grains were on the Shroud from its origin, this argument is spurious.











 When, in April 2004, the peer-reviewed, scientific Journal of Optics reported the discovery of a second face on the back of the Shroud it caused a firestorm of new interest in the Shroud. The Associated Press, the BBC and CNN fed the story around the world and newspapers wrote stories about it.
When, in April 2004, the peer-reviewed, scientific Journal of Optics reported the discovery of a second face on the back of the Shroud it caused a firestorm of new interest in the Shroud. The Associated Press, the BBC and CNN fed the story around the world and newspapers wrote stories about it. The amine vapors would also diffuse through the cloth and come in contact with the evaporation surface coating on the other side of the cloth. And this may help us further understand the picture of a second face on the back of the cloth.
The amine vapors would also diffuse through the cloth and come in contact with the evaporation surface coating on the other side of the cloth. And this may help us further understand the picture of a second face on the back of the cloth. The ghostlike picture on the left show how the picture of Jesus appears on the Shroud. When photographed with a film camera something quite startling emerges. If we look at negative before making a print we see a realistic picture of a man.
The ghostlike picture on the left show how the picture of Jesus appears on the Shroud. When photographed with a film camera something quite startling emerges. If we look at negative before making a print we see a realistic picture of a man.
































 David Farley is hot on the trail of Jesus’ foreskin, which has allegedly
David Farley is hot on the trail of Jesus’ foreskin, which has allegedly 








































